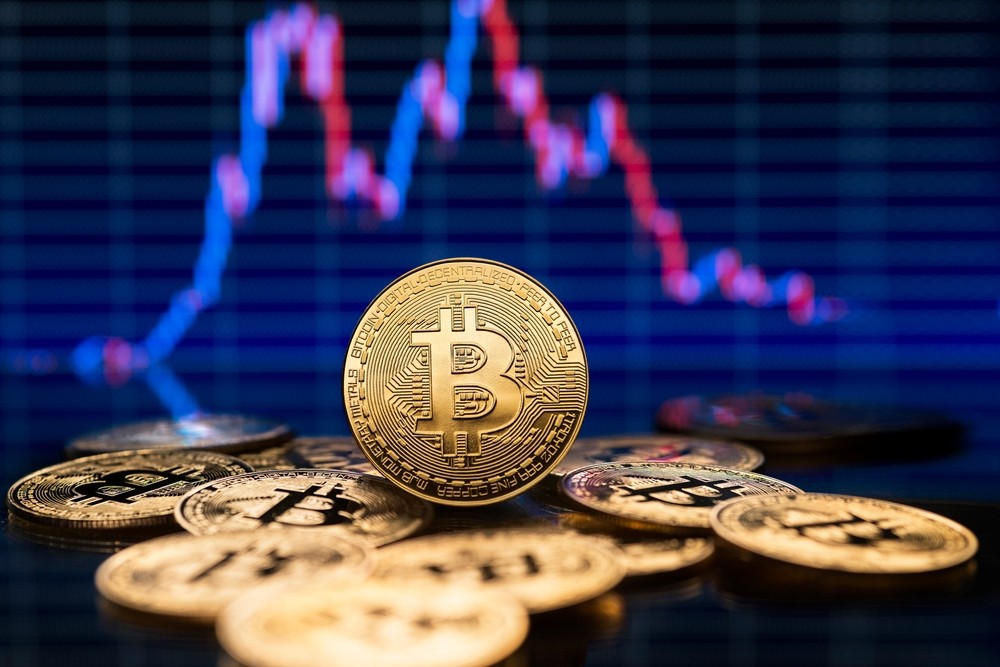
What is Bitcoin?
Bitcoin (BTC) is a currency, a decentralized virtual currency, and a payment system in itself. It does not need a bank or government as a central authority. In this way, third parties are eliminated from their transactions.
In 2008, Bitcoin was released to the public by an anonymous person or group, usually referred to as Satoshi Nakamoto. Up for the task, it has long since spread its popularity to become the most identifiable and used cryptocurrency and spur many more.
This guide contains Bitcoin history, bitcoin buying, bitcoin mining, and many other uses of Bitcoin.
Key Takeaways
- Although others have not confirmed this, Satoshi Nakamoto is known to be the author of Bitcoin; he introduced the design in 2008.
- Hence, it is a cryptocurrency created on a public blockchain and works according to that blockchain.
- They are trying to break the complicated cryptographic amount into the blockchain to receive Bitcoin as a reward for mining.
- Because Bitcoin has gained popularity, it is now used for trading, investing, and paying for goods and services.
- Investing in Bitcoin involves risks, such as loss of principal value, fraud, financial risk, and theft.
Understanding Bitcoin
In August 2008, when Satoshi Nakamoto was assembling Bitcoin, Martti Malmi’s contribution was registered at the domain Bitcoin.org.
How Bitcoin Started
So, in February 2009, Satoshi Nakamoto wrote a message on a cryptography list introducing a new peer-to-peer electronic cash system without a trusted third party. Next, the idea was drawn up on Bitcoin.org in a paper called Bitcoin: A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System. This document also goes on to be a foundation of how Bitcoin works today.
First Block
On January 3, 2009, a genesis block, the first Bitcoin block, was created. It contained a hint of allusion to that newspaper header and when the ice had been mined.
Rewards
Bitcoin rewards are decreased in half, or the number of block alliances halved to around 210,000. To see this, an initial reward in 2009 was 50 new bitcoins. The third halving was on May 11, 2020, when the amount of bitcoins to be rewarded per block was decreased to 6.25 bitcoins. The rewards were cut in half for the fourth time in April 2024, dropping to 3.125 BTC. The next halving will mark around mid-2028, followed by a reward dropping to 1.5625 bitcoin.
Denominations
One bitcoin has 8 decimal places of one bitcoin equaling 100 millionths. The satoshi is the smallest denomination.
Bitcoin’s Blockchain Technology
Bitcoin’s form as a digital currency is easy to understand. However, if you have Bitcoin, you can send fractions of that Bitcoin using your cryptocurrency wallet to buy goods or services. Bitcoin is very complex, and its main operating mechanism is indeed.
Blockchain
Now, it is a distributed ledger, in which each computer between an investigator’s and user’s machines will store the information in the middle. The meaning of distributed is so extreme that we don’t have any data stored on a centralized server; most data storage systems work on it.
Each computer is networked with the other via a network of automatic programs aboard each laptop to operate the blockchain and allow the necessary functions to automate the blockchain.
A blockchain is a file containing the block header and the transaction counter with the block listed. The block header includes some crucial elements, while the transaction counter contains the list of transactions in the particular block.
- In this context, the running blockchain is also known as the “magic number,” followed by its software version.
- It will serve as a replacement for the encrypted data saved on the previous block.
- All the hashed information from the previous transactions is called a Merkle Root. This hash is far too confusing until we explain it.
- It will enable us to determine which part of the content is contained in the block.
- It signaled the difficulty presently tackled by the miners to make a brand new block.
- A nonce is a number used only once. It solves the mining problem and opens the block.
After the encrypting process, information is introduced in all blocks, constituting the chain of encrypted blocks containing the information of all the previous blocks by the backway to the first block of the primary blockchain.
Encryption
This hashing algorithm encodes the information in Bitcoin’s blocks and blockchain. Data stored in a block can be seen as just a hashed version of the same for a blockchain.
In a byte representation, an individual 64-character hexadecimal number (256 bits) is a unique identifier with transaction data moving down on it, referred to as a separate block. The hash on this block is called the block’s hash and will link the blocks in the blockchain. It is data of the current block and all the previous transactions.
How to Buy Bitcoin
If you don’t want to mine Bitcoin, go on and select to buy it on a cryptocurrency exchange. First, it is easy (and even possible) to buy Bitcoin (BTC) with fiat (USD) through an exchange, but most won’t like purchasing that much Bitcoin as it is very expensive.
One way to buy Bitcoin is to create and fund an account on Coinbase using your bank account, debit card, or credit card, for example. The content will show you how to buy Bitcoin.
How to Mine Bitcoin
Mine Bitcoin has many ways, and hardware and software can be used. When the Bitcoin blockchain was first launched, it was possible to mine Bitcoin competitively with a single personal computer. But as its popularity increased and more miners joined the network, there were fewer and fewer chances of solving the hash.
If you have a newer piece of hardware than the one you are currently mining on, you can still use a personal computer, and your odds of solving a hash yourself are virtually nil.
Many miners are competing and hashing about 745 quintillion hashes per second (as of December 5, 2024). Machines specially designed for mining, namely ASICs, can generate several hundred trillion hashes per second. That is compared to a top-of-the-line personal computer that can make around 100 mega hashes per second, translating to 100 million hashes.
Options for Successful Mining
You can go for two hardware options as well as some software.
- You can use your existing computer and use mining software for Bitcoin that is compatible with Bitcoin and join a mining pool. Mining pools refer to groups of miners working together to compete with large ASIC mining machines. Although there are plenty of mining programs, as there are for mining pools, they are not very efficient or startup-friendly. BFGMiner and CGMiner are the two most popular among all the mining software. Foundry Digital, F2Pool, Antpool, Binance.com, and ViaBTC are some of the popular mining pools.
- Normally, if you can afford it, you buy an ASIC miner. New ASIC mining costs about $10,000, but miners upgrading their systems can sell or swap their existing or used models. Remember that buying one or more ASICs is not small and has high associated costs for electricity and cooling. While you will still not guarantee rewards, businesses will also be competing with you using one or two ASICs, Lagging behind thousands of ASICs operating on one master farm or several micro-farms, tens and hundreds of thousands of ASICs combined. CleanSpark claims to have 195,059 miners in operation, for example.
How to Use Bitcoin
Bitcoin was originally designed as a peer-to-peer payment system so people could send and receive money without using a bank. When it was first introduced, its developers envisioned this.
With Bitcoin’s value and popularity increasing, other cryptocurrencies and blockchain technologies also started appearing. Some of these new platforms came up with ideas similar to Bitcoin’s concept but expanded upon it, adding features that included faster transactions and smart contracts.
Payment
Today, many online and physical store businesses are ready to accept Bitcoin payments for their goods or services. QR codes, mobile apps, and direct wallet transfer methods can be used to make payments. Some companies even offer the opportunity to pay and use Bitcoin as an alternative to payment methods like credit cards or PayPal.
You will need a digital wallet to store your private key to use Bitcoin. Without these keys, you can’t make transactions or verify ownership.
Everyone’s interest increased as Bitcoin started being recognized. It was cheap in the early days, and its value grew incrementally. By 2017, its price was above $1,000, which attracted investors and traders.
Investing and Speculating
Many people in some countries thought Bitcoin could be a long-term investment and would only gain value over time. Some were in short-term trading; they bought and sold on crypto exchanges to make money from price variation.
Its price has been extremely volatile. In November 2021, it hit $69,000, declined to about $15,731 in 2022, and has been unable to break above $30,000 in 2023.
By early 2024, the excitement around the Bitcoin Spot ETF pushed its price into the mid-$ $40,000 range. When Bitcoin’s value surged past $50,000 again when these ETFs were officially approved in February 2024, it was the first time since January 3 that investors paid this much for a mega-cap.
Because investors consider Bitcoin another form of financial asset, Bitcoin prices tend to move in the same direction as the stock market. However, Bitcoin’s price swings are much more extreme, sometimes on a dime of thousands of dollars. Sharp price fluctuations occur in response to major news events that can affect prices, and many investors react quickly to such news events.
Risks of Investing in Bitcoin
The price of Bitcoin has had periods of major shifts. In 2019, it was $7,167, then jumped to $29,000 in 2020, peaked at $69,000 in 2021, dropped to $40,000, and returned to exceed $100,000 in 2024.
Because of these unpredictable price changes, most people buy Bitcoin as an investment, not for transactions. As it offers no guarantee and exists in a digital format, there are risks in owning and trading it.
Regulators such as SEC, FINRA, and CFPB have warned investors of these risks. On the front, some of the key concerns involve:
- Regulatory risk:Governments and financial agencies have not listed Bitcoin and other virtual currencies as currencies. As of December 2024, it is not officially counted as a security, but in the future (likely), regulations could affect how it is used or traded.
- Security risk:That is a security threat. They purchase and sell it on online exchanges. All these platforms are hackable, fail technologically, and suffer attacks from cyber crime syndicates, criminalizing the investment.
- Insurance risk:The funds you lose on bitcoins are not covered by FDIC or SIPC insurance and, therefore, may not be recoverable. Most exchanges, such as Coinbase and Gemini, offer little security breach coverage. Deposits made on such platforms may be FDIC ‘pass-through’ insured. You should always invest in the exchange’s protection policies before investing.
- Fraud risk: The more secure blockchain technology becomes, the less fraud risk is mitigated. However, weaknesses for scammers and fraud can exist.
- The market risk: Bitcoin is the same as any investment. Its value is up one day and down the next. Exchange volume and price movements of sharp assets have been increased. Additionally, it is very sensitive to price movements and responding to the news.
Regulating Bitcoin
As Bitcoin is so new and growing, it is hard to regulate. They don’t want to lose the economic wealth that cryptocurrency currently gives them; however, they would like to set some limits concerning cryptocurrency, as the US does.
Nevertheless, US enforcement agencies can work based on current securities, commodities, and taxation laws. This legislation was last adopted in 2024, and no new law was passed afterward.
But it finally replaced The European Commission with a bomb. However, it was reformed in 2023 by the already excessively awaited regulation of markets in crypto assets, the basis of which the European Union will regulate the cryptocurrency.
However, in December 2023, most of the cryptocurrency exchanges in India were banned, yet the government delayed taking action. Bitcoin and all other digital currencies have no desire to be regulated.
The Bottom Line
Bitcoin was the first cryptocurrency introduced to the public. It was supposed to be a way of payment outside the range of legal tender. Since its launch in 2009, Bitcoin has grown tremendously popular, and there have been increasing applications for it on the blockchain.
Investing in Bitcoin is easy, but the Bitcoin-generating process is complex. Investors on Bitcoin exchanges purchase Bitcoin, while speculators sell it. Investors need to seriously consider whether or not Bitcoin is a good investment option, especially like any investment, even when referring to the newest and most volatile investment—Bitcoin.
The contents published on Investopedia by its visitors are not Investopedia’s responsibility, and Investopedia can not be held accountable for any comments, opinions, or analyses available on the site. Warranty and liability disclaimer information can be found by referring to.
FAQs
What Exactly is Bitcoin and How Does It Work?
First, Bitcoin is a digital currency free of the auspices of a central authority. It is based on cryptography and, importantly, blockchain technology (blockchain) to protect its ledger.
What Happens If You Invest $100 in Bitcoin Today?
However, investing in Bitcoins and earning a profit is quite a risk. Its price changes almost every day (and its long-term performance remains unknown), and it can cost thousands of dollars.
Can You Convert Bitcoin Into Cash?
Most of the conventional currencies can be exchanged instead of Bitcoin.
How Much is $1 Bitcoin in US Dollars?
In turn, it can trade for 1 Bitcoin for a dollar equivalent. On December 5, however, BTC’s value fluctuated hugely, more than $100k during the day.
Read more business articles